The ABC’s of CPS (Common CPS Acronyms)
What do CPS terms mean?
When an allegation has been made that a child is being abused or neglected, it is the responsibility of the State to investigate and ensure the ongoing safety of the child. The CPS system is a veritable nightmare of government bureaucracy. Knowing the terminology may get you started, but having the right attorney on your side will get you through it.
A–D
E–H
J–M
N–R
S–Z
A–D
AAL: Attorney Ad Litem Attorney appointed by the Court to represent the interest of the child.
Abuse: “Abuse” includes the following acts or omissions by a person:
- (A) mental or emotional injury to a child that results in an observable and material impairment in the child’s growth, development, or psychological functioning;
- (B) causing or permitting the child to be in a situation in which the child sustains a mental or emotional injury that results in an observable and material impairment in the child’s growth, development, or psychological functioning;
- (C) physical injury that results in substantial harm to the child, or the genuine threat of substantial harm from physical injury to the child, including an injury that is at variance with the history or explanation given and excluding an accident or reasonable discipline by a parent, guardian, or managing or possessory conservator that does not expose the child to a substantial risk of harm;
- (D) failure to make a reasonable effort to prevent an action by another person that results in physical injury that results in substantial harm to the child;
- (E) sexual conduct harmful to a child’s mental, emotional, or physical welfare, including conduct that constitutes the offense of continuous sexual abuse of young child or children under Section 21.02, Penal Code, indecency with a child under Section 21.11, Penal Code, sexual assault under Section 22.011, Penal Code, or aggravated sexual assault under Section 22.021, Penal Code;
- (F) failure to make a reasonable effort to prevent sexual conduct harmful to a child;
- (G) compelling or encouraging the child to engage in sexual conduct as defined by Section 43.01, Penal Code, including conduct that constitutes an offense of trafficking of persons under Section 20A.02(a)(7) or (8), Penal Code, prostitution under Section 43.02(a)(2), Penal Code, or compelling prostitution under Section 43.05(a)(2), Penal Code;
- (H) causing, permitting, encouraging, engaging in, or allowing the photographing, filming, or depicting of the child if the person knew or should have known that the resulting photograph, film, or depiction of the child is obscene as defined by Section 43.21, Penal Code, or pornographic;
- (I) the current use by a person of a controlled substance as defined by Chapter 481, Health and Safety Code, in a manner or to the extent that the use results in physical, mental, or emotional injury to a child;
- (J) causing, expressly permitting, or encouraging a child to use a controlled substance as defined by Chapter 481, Health and Safety Code;
- (K) causing, permitting, encouraging, engaging in, or allowing a sexual performance by a child as defined by Section 43.25, Penal Code; or
- (L) knowingly causing, permitting, encouraging, engaging in, or allowing a child to be trafficked in a manner punishable as an offense under Section 20A.02(a)(5), (6), (7), or (8), Penal Code, or the failure to make a reasonable effort to prevent a child from being trafficked in a manner punishable as an offense under any of those sections.
ACR: Administrative Case Review If you do not agree with the way a CPS investigation was conducted, or you disagree with the findings of the investigation, and you believe your caseworker’s supervisor is not adequately addressing your concerns then you can request an administrative review of the investigation. If a review is granted, an Administrative Law Judge (ALJ) will review the actions of CPS and your caseworker; be prepared to specifically show how and why you believe your case was handled incorrectly. If there is a service plan in place, be prepared to show how your caseworker is violating the service plan.
ADA: Americans with Disabilities Act Federal law outlining specific protections against discrimination towards persons with disabilities. ADA Website
ADA: Assistant District Attorney In certain counties, the State’s interest is represented by the County or District Attorney. In Tarrant County CPS is represented by the District Attorney’s Office. They have a special unit of prosecutors located on Ben Avenue in Fort Worth that handle only CPS litigation.
Adversary Hearing: Following removal of a child from their home by DFPS, the court must hold a hearing within 14 days to revisit the issue of removal and either enter temporary placement orders or return the child to their family. If the court finds at this hearing that there is
- (1) Danger to the child’s physical health or safety and that it is contrary to the child’s welfare to remain in the home;
- (2) The urgent need for protection required immediate removal; and
- (3) That despite reasonable efforts to prevent or eliminate the need for removal and to return the child home, there is a substantial risk of continuing danger to the child in the home,
Then the court will enter temporary orders and appoint DFPS as the child’s temporary managing conservator.
A/N: Abuse/Neglect (also, CA/N: Child Abuse/Neglect) Alleged abuse or neglect can take many forms, and is defined in many different statutes. Abuse can be mental, emotional, physical and/or sexual. Neglect can be deliberate or unintentional. See Abuse and See Neglect
AOC: Aging Out of Care Youth living in foster care can remain there until they turn 18 (at which time they are legally considered an adult and CPS has no control over them). There are some exceptions for youth who want to stay in foster care after they turn 18, such as those who are attending high school, college or working on their GED certificate (known as Extended Foster Care). The Fort Worth area has the Transition Resource Action Center (TRAC Website) to help aged-out youth look for jobs, enroll in college courses and even receive emergency housing.
AOP: Acknowledgement of Paternity (see also Suit to Adjudicate Parentage) This is an affidavit, signed under oath by the child’s mother and father, acknowledging that the man claiming paternity is the biological father, and filed with the State Bureau of Vital Statistics (BVS). Such an acknowledgement can be made at any time and has the same effect as an adjudication of paternity (without having to go to court), but may be challenged within 4 years. Other ways to assign paternity: register with BVS before the child’s birth or within 31 days of birth; file suit to adjudicate parentage with AG’s office.
AP: Alleged Perpetrator
APS: Adult Protective Services Similar to CPS, APS is responsible for investigating allegations of abuse and neglect by individuals and care facilities on behalf of elderly or disabled adults.
AR: Alternative Response Following a lower risk report of abuse and/or neglect, a case can be assigned to the AR pathway. Unlike a traditional CPS investigation, this pathway is designed to be less adversarial and more collaborative, helping to address each family’s unique needs and get them back on track. This is a new approach (beginning in November 2014) and will take 2-3 years for statewide implementation.
ARD Committee/ARDC: Admissions, Review, and Dismissal Committee A group of people tasked by the Federal Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) with creating an Individualized Education Program (IEP) for children with disabilities. Members include the parent(s), school administrator, and general and special education teachers. The ARD Committee meets at least once during the school year to discuss educational goals for the child and develop a plan to achieve them.
AV: Alleged Victim
Baby Moses Law: Also known as a Safe Haven law. In Texas, a parent who is unable to care for their baby may take their unharmed baby (60 days old or younger) to any hospital, fire station or EMS station and tell an employee or personnel at that location that they want to leave the baby at a Safe Haven. A parent meeting these requirements will not be prosecuted for abandonment or neglect of the baby.
BVS/VSU: Bureau of Vital Statistics/Vital Statistics Unit The Texas BVS records important life events such as birth, death and adoption.
CAC: Child Advocacy Center Regional centers housing medical, law enforcement, social work and legal professionals who work in collaboration to aid in child abuse or neglect investigations.
CAFA: Court Appointed Family Advocate Attorney appointed by the Court to represent the interest of the parent. The parent has a right to have an attorney representing his/her interest, but the court will appoint an attorney in limited situations. For example, if the suit involves a request by CPS to terminate the parental rights and the parent is indigent, the parent can petition the Court to appoint an attorney. The parent also has a right to have an interpreter if the parent does not understand English or is hearing impaired.
CAPTA: Child Abuse Prevention and Treatment Act Federal legislation enacted in 1974 to define and address child abuse and neglect.
CASA: Court Appointed Special Advocate An outside party appointed by the Court to conduct an investigation of alleged child abuse or neglect; completes a report along with recommendations which are submitted for consideration to the Court. The CASA may also act as Guardian Ad Litem for the child. CASA Website
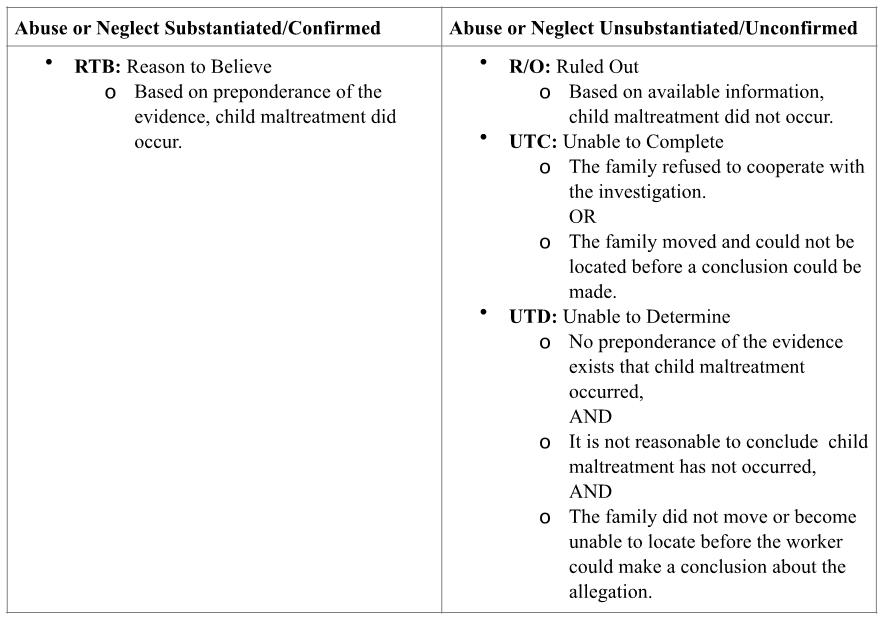
Case Disposition: After an initial investigation and case review, the case is given a final ruling (disposition): Abuse or Neglect Substantiated (Confirmed), or Abuse or Neglect Unsubstantiated (Unconfirmed). In cases where the abuse or neglect is substantiated/confirmed, the disposition assigned is “Reason to Believe.” In cases where the abuse or neglect is unsubstantiated/unconfirmed, the disposition assigned is “Ruled Out,” “Unable to Complete,” or “Unable to Determine.”
CBCAP: Community-Based Child Abuse Prevention Program “…informs parents of prevention services in their communities and encourages them to use them” including respite, parent education, fatherhood services, parent leadership, home visitation, and various special initiatives. Help for Parents, Hope for Kids Website
CCEJ: Court of Continuing and Exclusive Jurisdiction A court who issues a final order in a SAPCR acquires continuing and exclusive jurisdiction; no other court will have jurisdiction. Texas Family Code 155
CCL: Child Care Licensing Agency monitoring and regulating all childcare operations and child-placement agencies in Texas.
CFRT: Child Fatality Review Team Multidisciplinary and multiagency groups charged with reviewing child deaths on a local level from a public health perspective in order to identify prevention strategies and decrease the incidence of preventable child deaths.
Child Abuse Registry: A statewide registry of persons over 10 years of age who have been found “by a preponderance of the evidence to have committed an act of child abuse. Persons on the registry cannot hold certain jobs or volunteer with certain groups who serve children.
CHIP: Children’s Health Insurance Program Texas CHIP Medicaid
CIS: Communities in School A statewide program funded through the legislature to provide assistance to students at risk of dropping out of school. CIS of Texas Website
CLD: Closed Case designation when a case has been closed. A case can be closed for many different reasons, including dismissal of the abuse or neglect case, adoption of the child, or aging out by the child.
COL: Collateral Source/Contact A person who provides information in a CPS investigation about the alleged abuse, neglect and/or exploitation of the alleged victim(s) and their family. As long as this information is provided in good faith and for the purpose of assisting in the investigation, this person is immune from civil and criminal liability.
COS: Circles of Support This meeting is offered to youth (16 and older) to develop a transition plan for moving from substitute care to adulthood, and connect the youth with supportive and caring adults willing to help him/her after leaving substitute care. The youth is encouraged to bring together a broad spectrum of representatives from the youth’s support network, such as teachers, relatives, church members and friends. This meeting type is preferred over Transition Plan Meetings, but the youth may participate in both meetings over time. See also Transition Plan Meetings
CPS: Child Protective Services The purpose of CPS is to ensure the safety of all children, whether in a family or foster family environment. They do this by investigating allegations of abuse and/or neglect, removing the child from harmful situations, helping the family create a safe environment, and ultimately returning their child to their family, if possible, or placing the child with suitable caretakers. The ultimate goal of CPS is to keep the child with their family where possible. In extreme cases, CPS will seek to terminate the parent-child relationship. Texas CPS Website
CRCGs: Community Resource Coordination Groups Generally county-based, CRCGs pair local public agencies and private organizations to assist children, individuals and families who have multiple agency needs. CRCGs help identify needs that aren’t being met and then assist the individual or family in getting connected with service providers. There are also CRCGs for Adults (CRCGAs) and CRCGs for Families (CRCGFs).
CREST: Comprehensive Relative Enhancement, Support & Training National and State foster care research recognizes children will generally be better served by being placed with a relative (known as kinship placement or kin placement) rather than into a traditional paid foster care program. However, research also shows there are numerous challenges and fewer resources available for kinship caregivers. So kinship caregiver programs, such as CREST, were developed to provide services such as financial assistance and case management to reduce the likelihood a child will be returned to traditional paid foster care.
CRTs: Citizens Review Teams CRTs are made up of volunteer citizens who meet regularly around the state to review CPS investigations and ongoing interventions, evaluate casework and services provided, and issue reports to DFPS to help improve services and provide accountability.
CVS: Conservatorship When a child is removed by their home by CPS, the court appoints CPS as the child’s Conservator. CPS is legally responsible for the child’s welfare and assigns a Conservatorship caseworker.
CW: Caseworker CPS employee who is assigned to your case; your point of contact from the moment your child is removed from your home. They should regularly communicate with you about the nature of the abuse or neglect allegation; ask questions to conduct an investigation; monitor the health and well-being of the child during the removal; create a Service Plan outlining items that must be completed before your child is returned home or in order to close out the case.
CWA: Closed Without Assignment After an initial report of abuse or neglect has been made and the allegation has been reviewed, a supervisor or the investigation screener can close the case without assigning an investigator if it is found that there is not enough information to substantiate the allegation; the alleged victim or family cannot be located; the case is transferred to DFPS Adult Protective Services or another State agency; or the reported information has already been investigated.
CWB: Child Welfare Board CWBs serve to support CPS caseworkers by providing emergency resources for children who have been removed in the form of clothing, diapers, school supplies, etc. CWBs exist at the county and regional level, and are supervised by TCCWB, receiving training and updates on statewide policies and new legislation.
CWD: Children with Disabilities
CWLA: Child Welfare League of America The CWLA is a membership-based child welfare organization championing child welfare issues at the national level. CWLA Website
CYD: Community Youth Development “The CYD program contracts with community-based organizations to develop juvenile-delinquency prevention programs in ZIP codes with high juvenile crime rates for youth ages 6 to 17 (with a focus on youth ages 10 through 17).” Community Youth Development (CYD) Website
DADS: Texas Department of Aging and Disability Services A statewide agency created by the Legislature to provide services for elderly and disabled Texans. Formerly the Department of Human Services and the mental illness/disability part of MHMR. DADS Website
DARS: Department of Assistive and Rehabilitative Services A statewide agency created by the Legislature focused on ensuring that people with disabilities, and children who have developmental delays, enjoy the same opportunities as other Texans to live independent and productive lives. DARS includes four divisions: Rehabilitation Services, Blind Services, Early Childhood Intervention Services and Disability Determination Services DARS Website
DFPS: Texas Department of Family and Protective Services A statewide agency created by the Legislature to protect children, elderly adults, and adults with disabilities. DFPS is the parent-agency for CPS. DFPS Website
DISPRO: Disproportionality Across the US and in Texas, African American and Native American children are disproportionately affected by child abuse, children removed from their homes, children not returned to their home and placed in Foster Care, and children not adopted out of Foster Care. Texas recognizes this as a problem and has created working groups to evaluate the issue, make recommendations to the legislature, and implement best practices to reduce this disproportionality. Texas Disproportionality & Disparities Website
DNR: Do Not Resuscitate Order
DOB: Date of Birth
DPS: Department of Public Safety DPS Website
DSHS: Texas Department of State Health Services A statewide agency created by the Legislature that provides state-operated health care services, such as state mental hospitals, state-run health centers, and health agencies. Formerly the Department of Health, the mental health part of MHMR, Texas Health Care Information Council, and Texas Commission on Alcohol and Drug Abuse. DSHS Website
DSM-IV: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA); used by mental health professionals to evaluate and categorize mental health disorders in children and adults.
E–I
EA: Emergency Assistance
ECI: Texas Interagency Council on Early Childhood Intervention This now-defunct state agency was merged into DARS.
EMAB: Emotional Abuse See Abuse
Emergency Removal: When a child is removed from their home with no prior court order. DFPS must appear in court no later than the next business day and provide sufficient evidence of “a continuing danger to the physical health or safety of the child if returned to the home or evidence that the child has been sexually abused and is at substantial risk of future sexual abuse.”
ES: Educational Specialist In the Foster Care program, Education Specialists serve as education consultants to schools, case workers and foster parents to ensure the educational needs of children and youth in the program are met.
Extended Foster Care: Children over 18 who have aged-out of the foster care program can apply to remain in foster care if they are still in high school, working toward attaining their GED, or participating in other higher education programs.
FAD: Foster and Adoptive Home Development Program A DFPS program focused on recruiting, training, approving and verifying prospective foster and adoptive families in Texas.
Failure to Thrive: A very broad term used in the medical field for a child’s inability to gain weight or grow according to expected standards of growth. This can be brought on by illness, undernourishment or malnutrition.
FAS: Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (or FASD: Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders) FASD manifest in a range of disorders and severity; FAS is the most severe form of the condition affecting babies whose mothers consumed alcohol during early fetal development, especially during the first three months of pregnancy.
FBSS: Family-Based Safety Services Designed to maintain children safely in their homes (or to return children to their home), FBSS caseworkers help families evaluate their strengths and weaknesses, acquire necessary assistance and services, and stabilize the home to reduce the risk of future abuse or neglect. See also PCSP: Parental Child Safety Placement
FF: Foster Father
FGC: Family Group Conferences
FGDM: Family Group Decision Making This is a method CPS uses to include key family members in the safety and service planning decision making process, both before or after a child has been removed from a home. This method can be incorporated in Family Group Conferences (FGCs), Circles of Support (COS), and Family Team Meetings (FTMs).
FH: Foster Home
Foster Care: Children who have been temporarily or permanently removed from their home may be placed with pre-screened non-biological families to care for and provide services to the child.
FM: Foster Mother
FTM: Family Team Meeting Designed as a pre-removal quick response to child safety concerns by engaging family, community members and other caregivers in critical safety decisions, and are used to achieve positive outcomes for children in the earliest stages of DFPS involvement.
GAL: Guardian Ad Litem Person appointed by the Court to represent the interest of the child. This may be a family member or a CASA volunteer.
HHSC: Texas Health and Human Services Commission This State agency oversees the operations of the state’s health and human services, which is composed of five agencies: HHSC, DADS, DSHS, DARS and DFPS. HHSC Website
HIP: Project Help through Intervention and Prevention “Project HIP is a new effort that provides voluntary services to families that will increase protective factors and prevent child abuse. The program provides an extensive family assessment, home visiting programs that include parent education and basic needs support to targeted families. Eligible families are those who have previously had their parental rights terminated due to child abuse and neglect in year 2008 or later who currently have a newborn child, families who have previously had a child die with the cause identified as child abuse or neglect in year 2008 or later who have a newborn child, or current foster youth who are pregnant or who have given birth in the last four months.” Prevention and Early Intervention Programs Website
HOPES: Healthy Outcomes through Prevention and Early Support Program Community-based programs promoting child abuse prevention in families with children between 0-5 years of age.
HQ: Headquarters
HS: Home Study Prior to CPS placing a child in a Kinship Care or Foster Care home, a Home Study will take place to assess the home for children’s safety and available space, and must meet the Guidelines for Foster and Adoptive Home Studies. Home Study Guidelines
ICF/IID: Intermediate Care Facility for Individuals with an Intellectual Disability or Related Conditions This state program provides residential and habilitation services to people with intellectual disabilities and/or a related condition in a supervised 24-hour setting.
ICWA: Indian Child Welfare Act Federal legislation creating uniform statues and rules for granting jurisdiction to tribal governments in cases involving the removal of Native American children from their families.
IEP: Individualized Education Plan The IDEA mandates that Texas’ public education system must develop an IEP for every eligible child with a disability. Such a plan is developed using input from the child’s ARD Committee (which includes the child’s parent(s) and teachers).
IMPACT: Automated DFPS computer system for recording all case information. The program was implemented in 1996 and has been undergoing a modernization since 2014.
INS: Immigration and Naturalization Service Now-defunct federal agency under the U.S. Department of Justice regulating immigration and naturalization policy. In 2003 its functions were placed under the Department of Homeland Security and split into three new entities: U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), and U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP).
INV: Investigation
J–M
Kinship Care: When children have been removed from their home, it is CPS’ stated goal to place the children with a close family member, if appropriate accommodation can be made to care for the child and keep them safe.
LOC: Level of Care See Service Levels
MDNG: Medical Neglect See Neglect
MEPA: Multi Ethnic Placement Act Federal Law prohibiting state agencies from considering the race, color or national origin of a prospective foster or adoptive parent when placing a child of any race, color or national origin in foster or adoptive care.
MHMR: Texas Department of Mental Health and Mental Retardation Services are now provided under the Department of State Health Services through the Mental Health and Substance Abuse Division.
MHSA: Mental Health and Substance Abuse Division This division of DSHS provides statewide information and services related to behavioral health. MHSA Website
N–R
NCANDS: National Child Abuse and Neglect Data System A National database that collects and analyzes child abuse and neglect data as reported by all the CPS agencies in the U.S.
NCIC: National Crime Identification Center A national database of criminal justice information (e.g., criminal records, stolen property and missing persons); it is available to law enforcement agencies when running criminal background checks.
Neglect: “Neglect” includes:
(A) the leaving of a child in a situation where the child would be exposed to a substantial risk of physical or mental harm, without arranging for necessary care for the child, and the demonstration of an intent not to return by a parent, guardian, or managing or possessory conservator of the child;
(B) the following acts or omissions by a person:
(i) placing a child in or failing to remove a child from a situation that a reasonable person would realize requires judgment or actions beyond the child’s level of maturity, physical condition, or mental abilities and that results in bodily injury or a substantial risk of immediate harm to the child;
(ii) failing to seek, obtain, or follow through with medical care for a child, with the failure resulting in or presenting a substantial risk of death, disfigurement, or bodily injury or with the failure resulting in an observable and material impairment to the growth, development, or functioning of the child;
(iii) the failure to provide a child with food, clothing, or shelter necessary to sustain the life or health of the child, excluding failure caused primarily by financial inability unless relief services had been offered and refused;
(iv) placing a child in or failing to remove the child from a situation in which the child would be exposed to a substantial risk of sexual conduct harmful to the child; or
(v) placing a child in or failing to remove the child from a situation in which the child would be exposed to acts or omissions that constitute abuse under Subdivision (1)(E), (F), (G), (H), or (K) committed against another child; or
(C) the failure by the person responsible for a child’s care, custody, or welfare to permit the child to return to the child’s home without arranging for the necessary care for the child after the child has been absent from the home for any reason, including having been in residential placement or having run away.
Texas Family Code 261
Non-Emergency Hearing: After a report of abuse or neglect that CPS has determined does not require urgent removal of the child, DFPS can seek a court order asking for removal following an in-court hearing.
NSUP: Neglectful Supervision See Neglect
OAG: Texas Office of the Attorney General The OAG Child Support Division is responsible for the establishment of child support and enforcement of payments. The OAG Crime Victim Services is responsible for administering the Crime Victims’ Compensation Program. Texas OAG Website
Order in Aid of Investigation: The supervising Court may issue such an Order to compel cooperation with specific components of an investigation into abuse or neglect.
Order to Participate in Services: The supervising Court may issue such an Order to compel a parent or caretaker’s participation in services designed to avoid the need to remove a child from their home.
OV: Oldest Victim
P1: Priority 1 Classification These cases are considered to be high risk abuse, neglect and/or exploitation situations and require an initial investigation be conducted within 24 hours of their report. Such instances involve: Immediate rick of maltreatment that could result in death or serious harm to a child; Subsequent allegations of abuse or neglect received within 12 months after a previous investigation was closed as “Unable to Complete”; and/or An allegation that abuse or neglect led to a child’s death.
P2: Priority 2 Classification This is the next level of urgency for reports of abuse, neglect and/or exploitation situations and require an initial investigation be conducted within 72 hours of their report.
PN: Priority None Classification This is the final level of urgency for reports of abuse, neglect and/or exploitation situations and will not be recommended for investigation if the report involves past abuse or neglect, no current safety issues, no apparent risk of recurrence in the foreseeable future, or vital information is needed before the screener can make a determination whether an investigation is necessary.
Paternity Registry: The state paternity registry is maintained by the Vital Statistics Unit of DSHS to allow fathers to affirmatively assume responsibility for children they may have fathered.
PA: Program Administrator
PAL: Preparation for Adult Living Program A program run by DFPS to help prepare youth to transition out of the Foster Care system. The program instructs youth in areas such as independent living, financial independence, and continued education.
PC: Permanency Conference This type of meeting is used to develop or review the permanency plan for youth, and to identify, address or resolve barriers to achieving permanency. This is used when a FTM or FGC cannot be held for various reasons.
PCSP: Parental Child Safety Placement Some CPS cases can be resolved by temporarily placing the child/children with a family member or close friend while CPS works to stabilize the family and reduce the risk of future abuse or neglect. See also FBSS: Family-Based Safety Services
PD: Program Director
PD: Public Defender In some Texas counties (such as Dallas),the Public Defenders Office represents indigent defendants in matters involving felony and misdemeanor charges, CPS, mental health and appellate issues. In all criminal cases, accused persons who cannot afford to hire a defense attorney will receive one appointed by the court. During certain stages of a CPS case, the court may appoint an attorney to represent the parent.
PEI: Prevention and Early Intervention Programs DFPS programs focused on developing services within communities to prevent child abuse, delinquency, running away, truancy and dropping out of school. PEI Programs Website
PEP: Parents Empowering Parents Informal community groups led by parents who have been through the CPS process and successfully reunited with their child/children to provide information and answer questions for parents currently involved int he CPS process.
Permanency Planning: “Permanency” in the DFPS/CPS setting means a child leaving substitute (either kinship or foster) care and moving into an appropriate and permanent setting. This is a process that begins the moment a child is removed from their home and placed in substitute care. Permanency can be gained when a child is returned to their home, placed permanently with a family member, adopted, or the child ages out of care.
PHAB: Physical Abuse See Abuse
PJMC: Permanent Joint Managing Conservatorship When DFPS and the parent(s) or another person share Permanent Managing Conservatorship of the child; determined by the Court.
PMC: Permanent Managing Conservatorship When the Court severs the parent’s control and permanently places the child in the control of someone else (e.g., DFPS, a relative, or an adoptive parent).
PRIDE: Parent Resource for Information Development and Education A 35-hour training program for potential foster or adoptive parents.
PRN: Principal Source A person who is directly involved with providing information about the alleged abuse, neglect and/or exploitation of an alleged victim in a CPS investigation because of their involvement in the alleged abuse, neglect and/or exploitation. Usually, a parent or close family member.
RO: Ruled Out See Case Disposition
RTB: Reason to Believe See Case Disposition
RTC: Residential Treatment Center A general residential facility for 13 or more children requiring treatment services for emotional disorders.
S–Z
SACWIS: Statewide Automated Child Welfare Information System
SANE: Sexual Assault Nurse Examiner A registered nurse who has received specialized training in how to conduct a forensic sexual assault examination. This nurse can visually inspect the AV for sexual assault indicators, collect evidence that can be analyzed to determine the presence of certain bodily fluids, conduct an interview with the AV, and testify about the findings of the process and results in court.
SAPCR: Suit Affecting Parent-Child Relationship A case filed in court by an interested party (e.g., DFPS/CPS, a parent, a grandparent) asking the court to determine an issue such as custody of a child, visitation rights, child support, and medical treatment for a child.
Safety Plan: In instances where an allegation of abuse or neglect has been made and CPS has opened an investigation based on a determination of imminent or ongoing abuse/neglect, the CPS caseworker will work with the family to develop a Safety Plan. The Safety Plan is an agreement between you and CPS that you will do (or will refrain from doing) certain things to ensure the safety of your child.
SAVERR: System for Application and Verification of Eligibility Reporting and Review An HHSC information management system that was replaced by TIERS: Texas Integrated Eligibility Redesign System. See TIERS
SBS/AHT: Shaken Baby Syndrome/Abusive Head Trauma SBS is caused when an infant or small child is violently shaken or their head is impacted, causing a variety of injuries or even death.
Service Levels: All children who are placed in substitute care are evaluated by the CPS caseworker and supervisor or a third party contractor to determine the individual service needs of the child and to find an appropriate substitute care placement. The service levels are Basic, Moderate, Specialized, or Intense.
Basic Service Level: A supportive setting, preferably in a family that is able to maintain or improve the child’s functioning.
Moderate Service Level: A structured supportive setting, preferably in a family, in which most activities are designed to improve the child’s functioning.
Specialized Service Level: A treatment setting, preferably in a family, in which caregivers have specialized training to provide therapeutic, habilitative, and medical support and interventions.
Intense Service Level: A high degree of structure, preferably in a family, to limit the child’s access to environments as necessary to protect the child. The caregivers have specialized training to provide intense therapeutic and habilitative supports and interventions with limited outside access.
All information retrieved from DFPS Website.
Service Plan: A detailed document created by the CPS caseworker identifying the child’s safety needs, permanency goals, and steps towards attaining the permanency goals.
SI: Special Investigation CPS Investigator positions created in 2005 intended for persons with prior law enforcement experience. Ideally, these SI’s would be better equipped to use their forensic investigative skills to track and evaluate the toughest CPS cases.
SIB: Sibling
SIDS: Sudden Infant Death Syndrome The sudden and unexplained death of an infant younger than 1 year old.
SIL: Supervised Independent Living A non-traditional and less-restrictive housing placement for young adults still participating in extended foster care; allows youths to practice independent living and self-sufficiency skills with minimal supervision and case management.
SSA: Social Security Administration
SSI: Social Security Income
STAR: Services to At-Risk Youth Includes family crisis intervention counseling, short-term emergency respite care, and individualized family counseling for youth ages 7-17 who experience conflict at home, have been truant or delinquent, or have run away, and their families.
Status Hearing: Must be held no later than 60 days after a temporary order is entered by the court: to evaluate the contents of the service plan; designate the person authorized to give medical consent for the child; inform the court of diligent search efforts for any missing parents; and warn parents that their parental rights could be terminated unless the parent can offer the child a safe environment.
SUP: Supervisor
Suit to Adjudicate Parentage: A suit often brought by the Attorney General’s Office (but can also be brought by another person such as the child’s mother or legal guardian), generally to hold the child’s father financially responsible for the child.
SWI: Statewide Intake A division within DFPS of intake specialists who receive and review reports of child abuse, neglect and exploitation. These specialists determine whether or not the reported information warrants DFPS involvement. If so, the case is referred to the correct jurisdiction. If not, they may refer the reporting person to other available services.
SXAB: Sexual Abuse See Abuse
SYSN: Statewide Youth Services Network Community-based programs aimed at reaching at-risk youth 6-17 years of age to prevent truancy and delinquency, curb interaction with tobacco, alcohol or illegal drugs, and avoid contact with the juvenile justice system.
TAC: Texas Administrative Code Statute that codifies rules for all state agencies in Texas. Texas Administrative Code
TACFS: Texas Alliance of Child and Family Services (Formerly TALCS: Texas Association of Leaders in Children and Family Services) TACFS Website
TANF: Temporary Aid to Needy Families Cash assistance provided to families by HHSC based on financial need.
TARE: Texas Adoption Resource Exchange An online database created by DFPS to provide information to persons and families interested in adopting.
TCCWB: Texas Council of Child Welfare Boards See Child Welfare Board (CWB)
TEA: Texas Education Agency State agency overseeing primary and secondary public education and its institutions. TEA Website
Texas Abuse Hotline: To report abuse, neglect, or exploitation of children, the elderly or people with disabilities, please call 1-800-252-5400.
Texas Youth and Runaway Hotlines: The toll-free Texas runaway Hotline (1-888-580-HELP) and the Texas Youth Hotline (1-800-210-2278) offer crisis intervention, telephone counseling, and referrals to troubled youth and families.
TFC: Texas Family Code Codification of all laws affecting family relationships in Texas. Texas Family Code
TFTS: Texas Families: Together and Safe This program funds community-based programs that alleviate parental stress, promote parental competency, and increase child nurturing while working toward family self-sufficiency.
TIERS: Texas Integrated Eligibility Redesign System An information management system used by HHSC to process service eligibility determinations.
TIFI: Texas Integrated Funding Initiative A collaborative system for state and private sector agencies and programs to provide services to families with children who have complex mental health needs.
TJJD: Texas Juvenile Justice Department (Formerly TJPC: Texas Juvenile Probation Commission and TYC: Texas Youth Commission) State agency overseeing the treatment and rehabilitation of juvenile offenders living in TJJD facilities and halfway houses.
TJMC: Temporary Joint Managing Conservatorship When DFPS and the parent(s) or another person temporarily share Managing Conservatorship of the removed child; determined by the Court.
TJPC: Texas Juvenile Probation Commission See TJJD: Texas Juvenile Justice Department
TLS: Transitional Living Services A program that administers services for substitute care youth ages 14-23 such as Circles of Support, PAL, and Extended Foster Care.
TMC: Temporary Managing Conservatorship When the Court places the child under DFPS’s control; the child may remain in their home under certain restrictions from the Court designed to ensure the child’s safety, or the Court may remove the child from the home based on allegations of abuse or neglect. DFPS becomes temporarily responsible for making decision on behalf of the child.
TNOYS: Texas Network of Youth Services An association of youth services providers. TNOYS Website
TO: Temporary Order A decision issued by a court to temporarily set the status quo. Any TO’s issued by a court must be followed until a subsequent hearing is held or final orders are entered. In a CPS removal case, the court may issue a TO establishing temporary custody/conservatorship of a child.
TPR: Termination of Parental Rights During a CPS investigation, if the parent(s) is perpetually unable to provide or maintain a safe home for the child, DFPS may ask the court to terminate parental rights; this is generally requested as an alternative resolution in DFPS’ original SAPCR filing with the court so that the parent(s) is on notice of the potential for losing legal rights to their child.
TPM: Transition Plan Meeting If a youth declines to have a Circle of Support (COS) or one cannot be held, a TPM is held as an alternative. This mirrors a COS meeting but will have fewer participants and is a more DFPS-driven conference. See also Circles of Support
TSD: Texas School for the Deaf TSD Website
TWC: Texas Workforce Commission TWC Website
TYC: Texas Youth Commission See TJJD: Texas Juvenile Justice Department
UCCJEA: Uniform Child Custody Jurisdiction Enforcement Act Federal statute which determines a child’s “home state” with regard to jurisdiction for child custody litigation.
UTC: Unable to Complete See Case Disposition
UTD: Unable to Determine See Case Disposition
YFT: Youth for Tomorrow A non-profit agency contracted by DFPS to evaluate the service needs of children in substitute care. YFT Website